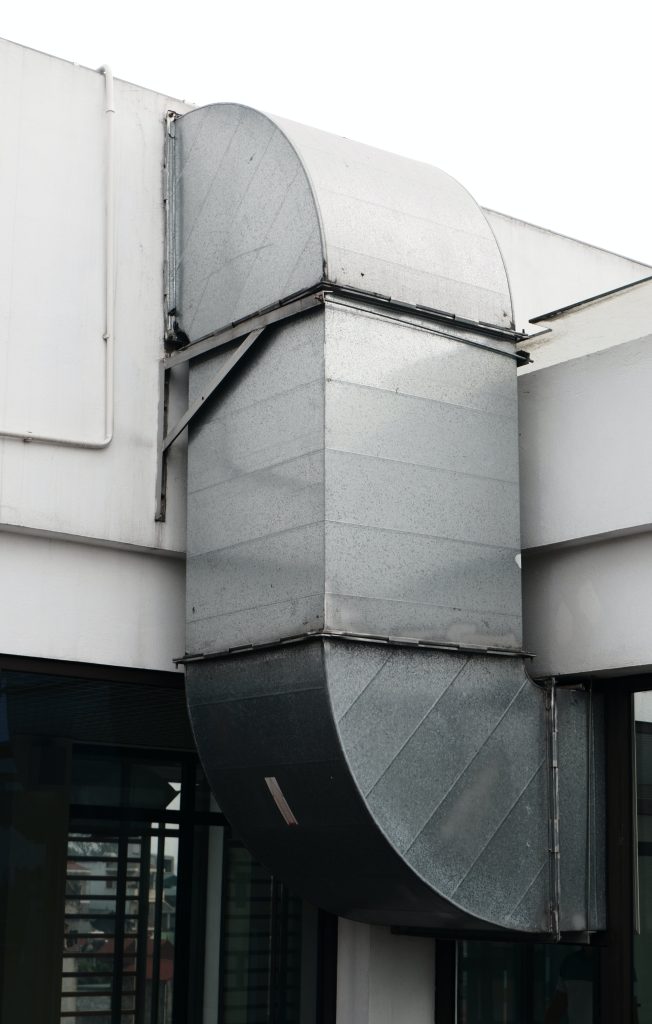
Venting in construction refers to the process of providing openings or pathways for the exchange of air or gases within a building or structure. Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining indoor air quality, controlling moisture levels, and ensuring the health and safety of occupants. Ventilation systems are designed to remove stale air, pollutants, and excess moisture while bringing in fresh air from the outside.
Here are some key aspects of venting in construction:
- Natural Ventilation: This involves using natural forces, such as wind and temperature differences, to facilitate the movement of air. Windows, doors, and vents may be strategically placed to take advantage of natural ventilation.
- Mechanical Ventilation: Mechanical ventilation systems use fans or other mechanical devices to circulate air. These systems are commonly found in buildings where natural ventilation is insufficient or impractical.
- Types of Vents:
- Roof Vents: Designed to allow air to escape from the attic space, preventing the buildup of heat and moisture.
- Wall Vents: Placed in exterior walls to allow air exchange between the interior and exterior of a building.
- Soffit Vents: Located in the eaves of a roof, these vents allow air to flow into the attic space.
- Ridge Vents: Installed along the peak of a roof to promote air circulation and prevent heat buildup.
- Foundation Vents: Placed in the foundation walls to allow air circulation in crawl spaces.
- Purpose of Venting:
- Air Quality: Ventilation helps remove pollutants, odors, and indoor contaminants, ensuring a healthier indoor environment.
- Moisture Control: Adequate venting prevents the buildup of moisture, which can lead to mold growth and structural damage.
- Temperature Regulation: Ventilation contributes to temperature control by allowing the exchange of warm and cool air.
- HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems play a crucial role in controlling indoor air quality and temperature. These systems often include ventilation components to ensure the proper exchange of air.
- Ductwork: In buildings with forced-air HVAC systems, ductwork is used to distribute air to various rooms. Proper design and installation of ductwork are essential for efficient ventilation.
- Building Codes: Ventilation requirements are often specified in building codes to ensure that buildings meet minimum standards for indoor air quality and safety.
- Occupancy Considerations: The ventilation needs of a building are influenced by factors such as the number of occupants, the type of activities conducted within, and the size and layout of the space.
Effective venting is a critical component of a well-designed building, contributing to the comfort, safety, and longevity of the structure while promoting a healthy indoor environment. Designing and implementing an appropriate ventilation system depend on the specific requirements of the building and its intended use.